Alpha, beta and gamma:
.
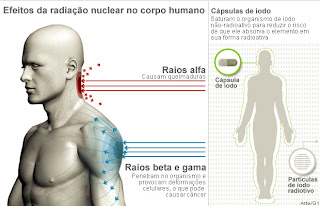
Alpha radiation can not penetrate the body; it causes a skin burn; the beta and gamma radiation - mainly gamma - enter the body and cause cellular deformation.
This is the same gamma radiation used in radiotherapy treatments, just to fight cancer. At low doses, it destroys tumors. At high, it can cause cell damage that leads to cancer.
The radioactivity can affect health in two main ways: When is ionizing, means: It is capable of changing the chemical structure of substances. With this, it changes the characteristics of common substances in our body; from the water, for example, it can form free radicals, which, in excess impairs the body's functioning.
Another possibility is that nuclear radiation directly affects the cells. The change in chemical structure of the elements can represent, for example, breaking of the DNA chain.
The modern medicine, still, can not tell if there is a limit amount of radiation to which the body must be exposed to such effects could develop cancer.
Exposure to rays is not the only risk to which the human body is subjected in relation to radioactivity. It is even more important to prevent people incorporate radioactive material. The most common way this happens is by inhalation of gases that mingle with the atmosphere after a leak.
One element that represents a bigger threat in this sense is iodine. The human body needs it to function normally and the thyroid tends to absorb radioactive iodine particles that are suspended in the air. To prevent this, are being given pills non-radioactive iodine to the population. Thus, the body becomes saturated and the element, even if it is inhaled in radioactive form, will not be absorbed.
The meltdown of a nuclear reactor does not kill people like a bomb. What kills even in case of a nuclear bomb is not the radiation, is the shock wave, then the heat wave and finally the radiation. Intensity of radioactive material in a nuclear bomb is much greater because the energy spent is very large and has no barrier. Yet, a reactor has four barriers against the release of nuclear material into the environment.
.
Alpha radiation can not penetrate the body; it causes a skin burn; the beta and gamma radiation - mainly gamma - enter the body and cause cellular deformation.
This is the same gamma radiation used in radiotherapy treatments, just to fight cancer. At low doses, it destroys tumors. At high, it can cause cell damage that leads to cancer.
The radioactivity can affect health in two main ways: When is ionizing, means: It is capable of changing the chemical structure of substances. With this, it changes the characteristics of common substances in our body; from the water, for example, it can form free radicals, which, in excess impairs the body's functioning.
Another possibility is that nuclear radiation directly affects the cells. The change in chemical structure of the elements can represent, for example, breaking of the DNA chain.
The modern medicine, still, can not tell if there is a limit amount of radiation to which the body must be exposed to such effects could develop cancer.
Exposure to rays is not the only risk to which the human body is subjected in relation to radioactivity. It is even more important to prevent people incorporate radioactive material. The most common way this happens is by inhalation of gases that mingle with the atmosphere after a leak.
One element that represents a bigger threat in this sense is iodine. The human body needs it to function normally and the thyroid tends to absorb radioactive iodine particles that are suspended in the air. To prevent this, are being given pills non-radioactive iodine to the population. Thus, the body becomes saturated and the element, even if it is inhaled in radioactive form, will not be absorbed.
The meltdown of a nuclear reactor does not kill people like a bomb. What kills even in case of a nuclear bomb is not the radiation, is the shock wave, then the heat wave and finally the radiation. Intensity of radioactive material in a nuclear bomb is much greater because the energy spent is very large and has no barrier. Yet, a reactor has four barriers against the release of nuclear material into the environment.
good post
ReplyDeletethanks Rosane